Are You Ready for the European Health Data Space?
Don’t miss the opportunity to help make data more accessible to healthcare providers, researchers, and government agencies – and grow your business.
BlueStar's diverse portfolio offers unparalleled access to premium products and services that drive business growth and success. From state-of-the-art hardware to advanced software solutions, our portfolio is designed to empower businesses with the tools they need to thrive in today's competitive landscape.
Our vertical-based content focuses on different industry technologies, solutions, and insights.
A true VAD offers top-notch pick, pack and ship services, and provides programs and services that add value to the distributed products that increase their value or worth.
The BlueStar Difference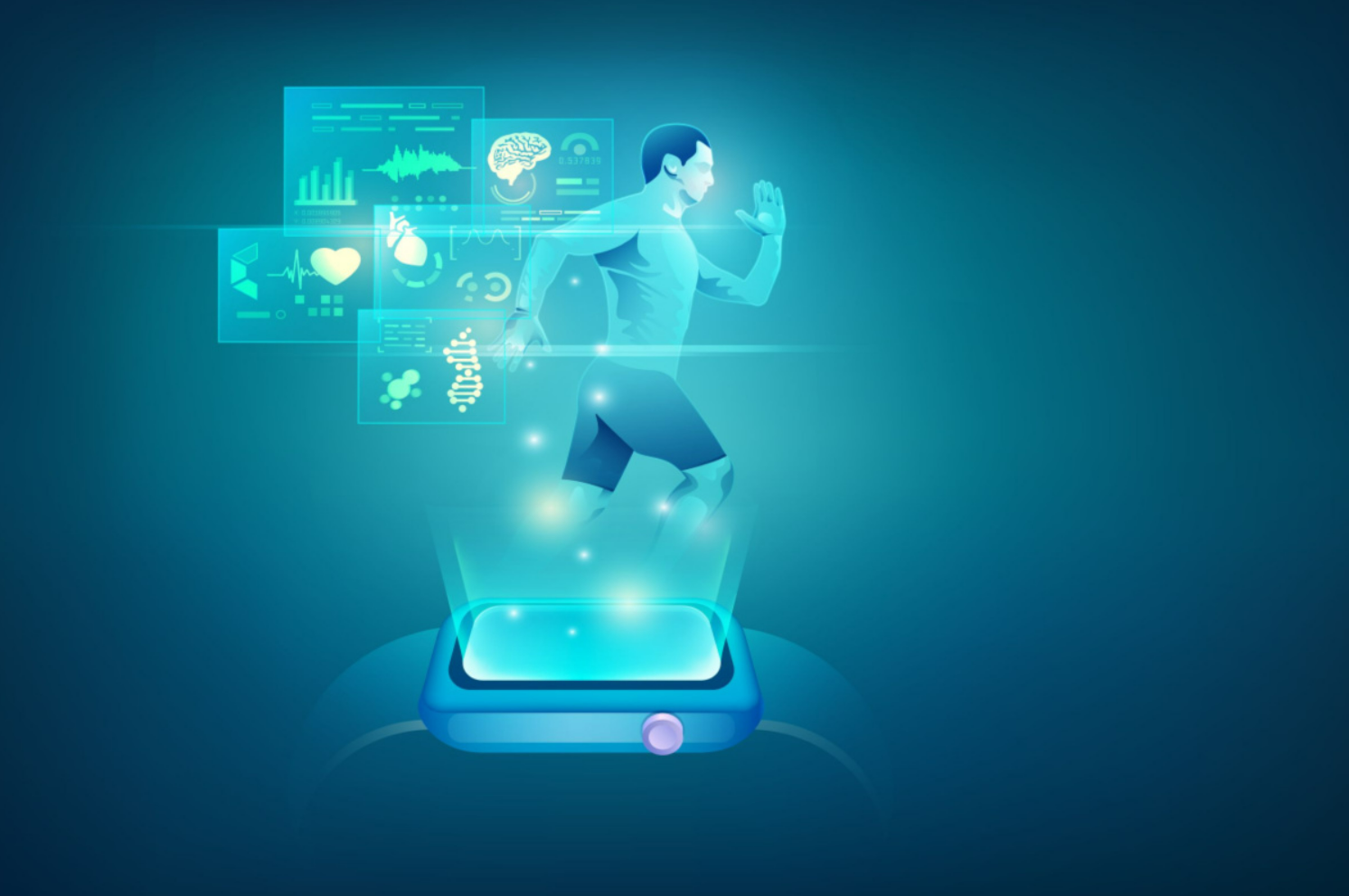
Healthcare providers need your expertise to implement reliable systems that collect vital patient data.
Healthcare providers strive to provide the highest level of care using modern technology. Today that includes implementing solutions leveraging healthcare wearables. These solutions have evolved to the point of personalization and affordability that enables access to data from the patient that can be leveraged to make better treatment decisions. In a recent HIMSS survey, more than half of healthcare professionals stated that wearable technology is helpful in monitoring vitals, tracking medications, following up post-op recovery, and logging sleep quality.
With increasing healthcare wearables adoption on the horizon, technology solution providers must ensure they support this trend to meet demand and remain relevant.
Healthcare wearable devices (HWDs) can be classified into three categories:
These healthcare wearables monitor physiological and psychological vitals to treat cardiovascular and neuromuscular diseases. For example, textile based HWDs embed sensors in clothing to monitor parameters such as body temperature, heart rate, and respiration. Tatoo-based HWDs involve embossing graphene electronic tattoos onto the skin to help diagnose abnormalities like cardiovascular arrhythmias.
Biomarkers in sweat, saliva, tears, and urine are essential for healthcare diagnostics. Wearables help monitor these biomarkers and their concentration to ensure they remain within acceptable levels. In addition, these HWDs can alert patients to fluctuations in biomarker levels, so they can take quick action before conditions become critical.
Made from biodegradable and biocompatible materials, these wearables can be used to deliver medication in a controlled manner. Depending on the disease, different wearables can be applied, including smart contact lenses for ocular treatments or monitoring and self-healable gums for oral delivery. Additionally, smart bandages and touch-actuated transdermal delivery work together to provide a controlled amount of medication released via microneedles upon touching a sensor.
For years patients often had to use expensive, complicated, and uncomfortable methods for self-monitoring of vitals or had to be inconvenienced by frequent trips to the healthcare provider’s office. In addition, legacy processes provided only fragmented data collected at the time practitioners checked vital signs or biomarker levels. However, with wearables, patients can now comfortably and affordably monitor 24/7. This allows for more consistent, accurate data for analysis to deliver more personalized treatment to the patient.
As healthcare wearables evolve, solution providers will hold the key to bridging the gap between gathering data and being able to interpret it and deliver insights to healthcare providers’ technology, including:
Internet of Things (IoT): This system connects healthcare wearables to a network that shares and uses the data. Intelligent systems can immediately analyze data and trigger alerts or actions. However, many systems aren’t designed for wearables, so you may need to develop or partner to create an interface for wearables to work with the system.
Artificial Intelligence: Data collected means nothing unless the system is large enough to manage, analyze, and prioritize information. Better data and analysis with artificial intelligence (AI) allow healthcare providers to make more informed decisions faster when treating the patient and improving patient outcomes.
Cybersecurity: Sensors, wearables, and IoT devices are cyberattack targets, and malware can have devastating consequences for patient health and healthcare networks. Providing your clients with cybersecurity solutions can help keep these systems and patients safe.
5G: 5G systems have lower latency (from 20 milliseconds with 4G to 1 millisecond with 5G). They can support more devices per square area, making healthcare wearables a viable solution for large patient populations.
Your clients need your expertise to create systems capable of accurately and reliably collecting data for patient monitoring and alerts that improve patient outcomes. Provide healthcare wearables solutions on the cutting edge and improve the critical connection between patients and providers.
Don’t miss the opportunity to help make data more accessible to healthcare providers, researchers, and government agencies – and grow your business.

Emerging identification technologies are shaping the future of hospital check-in. Here’s why technology solutions providers (TSPs) are key to...
How European TSPs can drive patient safety and efficiency with barcoding solutions for blood traceability.